Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
automatic differentiation#
Basic demonstration of AutoDiff with pymiediff
author: P. Wiecha, 03/2025
imports#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import pymiediff as pmd
backend = "torch" # "scipy" or "torch"
setup#
we setup the particle dimension and materials as well as the environemnt. This is then wrapped up in an instance of Particle.
For all input parameter that we later want to calculate gradients, we set requires_grad = True
# - config
wl0 = torch.linspace(500, 1000, 50)
wl0.requires_grad = True
k0 = 2 * torch.pi / wl0
r_core = torch.as_tensor(70.0)
r_core.requires_grad = True
r_shell = 100.0
mat_core = pmd.materials.MatDatabase("Si")
mat_shell = pmd.materials.MatDatabase("Ge")
n_env = 1.0
# - setup the particle
p = pmd.Particle(
r_core=r_core,
r_shell=r_shell,
mat_core=mat_core,
mat_shell=mat_shell,
mat_env=n_env,
)
print(p)
core-shell particle
- core radius = 70.0nm
- shell radius = 100.0nm
- core material : Si
- shell material : Ge
- environment : eps=1.00
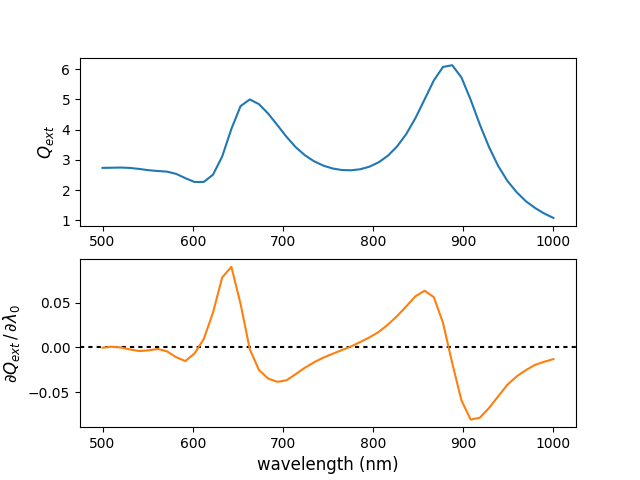
gradients with respect to wavelength#
Calculate the gradients of the extinction wrt the input wavelengths
cs = p.get_cross_sections(k0, backend=backend)
q_ext = cs["q_ext"]
# - gradient of each Q_ext wrt the wavelength
qext_grad_wl = torch.autograd.grad(
outputs=q_ext, inputs=wl0, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(q_ext), retain_graph=True
)[0]
print("grad wrt wavelength:", qext_grad_wl)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(wl0.detach().numpy(), q_ext.detach().numpy())
plt.ylabel(r"$Q_{ext}$", fontsize=12)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.axhline(0, dashes=[2, 2], color="k")
plt.plot(wl0.detach().numpy(), qext_grad_wl.detach().numpy(), color="C1")
plt.xlabel("wavelength (nm)", fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel(r"$\partial Q_{ext} \, /\, \partial \lambda_0$", fontsize=12)
# plt.savefig("ex_03a.svg", dpi=300)
plt.show()
/home/runner/work/MieDiff/MieDiff/src/pymiediff/materials/mat.py:388: UserWarning: Converting a tensor with requires_grad=True to a scalar may lead to unexpected behavior.
Consider using tensor.detach() first. (Triggered internally at /pytorch/torch/csrc/autograd/generated/python_variable_methods.cpp:836.)
wl_key = float(wavelength)
grad wrt wavelength: tensor([-2.9321e-04, 7.7116e-04, -8.7224e-05, -2.3012e-03, -4.0959e-03,
-3.2819e-03, -1.7332e-03, -4.3679e-03, -1.0955e-02, -1.5276e-02,
-6.7180e-03, 9.4561e-03, 3.8904e-02, 7.8404e-02, 9.0289e-02,
4.8767e-02, -2.0686e-03, -2.5291e-02, -3.4930e-02, -3.8558e-02,
-3.6785e-02, -2.9879e-02, -2.2654e-02, -1.6573e-02, -1.1373e-02,
-7.1579e-03, -3.0049e-03, 1.0508e-03, 6.0219e-03, 1.1223e-02,
1.7293e-02, 2.5442e-02, 3.5040e-02, 4.5952e-02, 5.7278e-02,
6.3571e-02, 5.6280e-02, 2.7473e-02, -1.7607e-02, -5.9238e-02,
-8.0823e-02, -7.8771e-02, -6.7885e-02, -5.4685e-02, -4.1747e-02,
-3.2469e-02, -2.5396e-02, -1.9532e-02, -1.6047e-02, -1.3047e-02])
gradients with respect to core radius#
Calculate the gradients of the extinction wrt the particle core radius.
Note that reverse mode autodiff requires one backwards pass per output scalar.
# - gradients of each Q_ext (every wavelength) wrt core radius
qext_grad_rcore = []
for q_wl in q_ext:
qext_grad_rcore.append(
torch.autograd.grad(
outputs=q_wl, inputs=len(q_ext) * [r_core], retain_graph=True
)[0]
)
qext_grad_rcore = torch.stack(qext_grad_rcore)
print("grad wrt core radius:", qext_grad_rcore)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(wl0.detach().numpy(), q_ext.detach().numpy())
plt.ylabel(r"$Q_{ext}$", fontsize=12)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.axhline(0, dashes=[2, 2], color="k")
plt.plot(wl0.detach().numpy(), qext_grad_rcore.detach().numpy(), color="C1")
plt.xlabel("wavelength (nm)", fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel(r"$\partial Q_{ext} \, /\, \partial r_{core}$", fontsize=12)
# plt.savefig("ex_03b.svg", dpi=300)
plt.show()
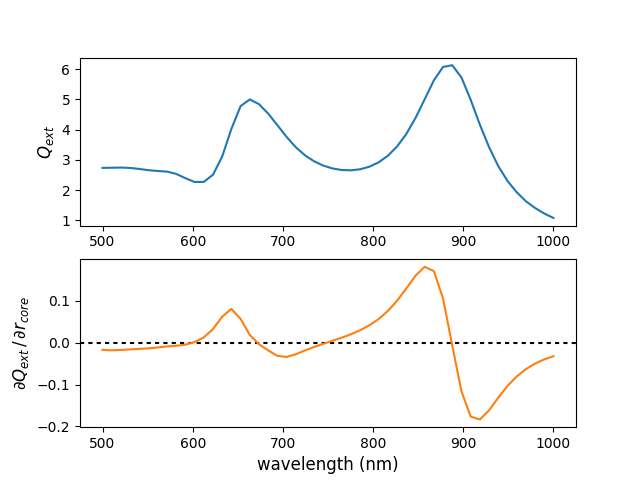
grad wrt core radius: tensor([-0.0170, -0.0181, -0.0172, -0.0159, -0.0147, -0.0134, -0.0113, -0.0089,
-0.0073, -0.0047, 0.0016, 0.0129, 0.0326, 0.0624, 0.0808, 0.0571,
0.0186, -0.0035, -0.0183, -0.0313, -0.0340, -0.0275, -0.0185, -0.0100,
-0.0025, 0.0047, 0.0122, 0.0203, 0.0299, 0.0417, 0.0567, 0.0758,
0.1004, 0.1296, 0.1602, 0.1816, 0.1715, 0.1060, -0.0062, -0.1158,
-0.1765, -0.1838, -0.1618, -0.1315, -0.1036, -0.0810, -0.0632, -0.0500,
-0.0399, -0.0322])
Gradients of Mie coefficients#
Using the lower level functions, we can also calculate gradients of Mie coefficients
# - some radii and ref.index particle config for this demo
wl0 = [500.0] # nm
k0 = 2 * torch.pi / torch.as_tensor(wl0)
n_c = torch.as_tensor(3.0)
n_s = torch.as_tensor(4.0)
r_c = torch.as_tensor(110.0) # nm
r_s = torch.as_tensor(130.0) # nm
r_s.requires_grad = True
# which Mie order to evaluate (Note: supports vectorization)
n_max = 2
gradient wrt abs. of Mie coefficient#
How to calculate gradient wrt magnitude of Mie coefficient. May be useful to suppress or maximize a specific Mie mode.
mie_coef_result = pmd.coreshell.mie_coefficients(
k0=k0, r_c=r_c, eps_c=n_c**2, r_s=r_s, eps_s=n_s**2, eps_env=1.0, n_max=n_max
)
a_n = mie_coef_result["a_n"]
abs_a_n = torch.abs(a_n[-1, :]) # evalulate last available order
abs_a_n.backward(retain_graph=True)
print("|a_2|:", abs_a_n)
print(
"grad:",
r_s.grad,
": change the shell radius into this direction will reduce |a_n|.",
)
|a_2|: tensor([[0.8582]], dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<AbsBackward0>)
grad: tensor(0.1169) : change the shell radius into this direction will reduce |a_n|.
gradient wrt complex Mie coefficient#
Calculate gradients of complex values requires to evaluate real and imaginary parts separately. The respective partial derivatives are the real and imag part of the gradient.
mie_coef_result = pmd.coreshell.mie_coefficients(
k0=k0, r_c=r_c, eps_c=n_c**2, r_s=r_s, eps_s=n_s**2, eps_env=1.0, n_max=n_max
)
# use first particle and first wavelength. Coeff. shape is (n_mie, n_particle, n_k0)
b_n = mie_coef_result["b_n"][:, 0, 0]
# evaluate real and imag part separately of Mie coefficient (of highest order)
grad_bn_real = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=b_n[-1].real, inputs=r_s, retain_graph=True)[
0
]
grad_bn_imag = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=b_n[-1].imag, inputs=r_s, retain_graph=True)[
0
]
print("b_2", b_n[-1])
print("grad:", "Re:", grad_bn_real, "Im:", grad_bn_imag)
b_2 tensor(0.0324+0.1770j, dtype=torch.complex128, grad_fn=<SelectBackward0>)
grad: Re: tensor(-0.0006) Im: tensor(-0.0015)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.145 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 601 MB
